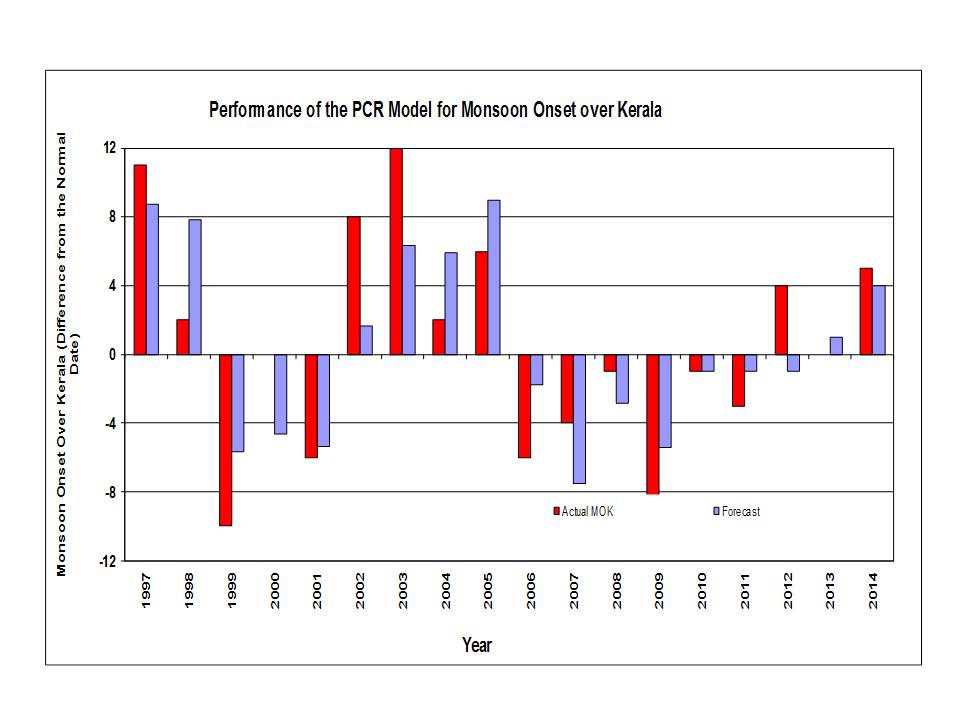
Prediction of monsoon onset date over Kerala
A model based on principle component regression (PCR) technique is used for the prediction of monsoon onset over Kerala (MOK). The details of the 6 predictors are given below.
| S. No | Name of the Predictor | Temporal Domain | Geographical Domain | C.C 1975-2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SE Indian Ocean SST anomaly | JAN | 24S-14S, 80E-100E | 0.41 |
| 2 | NW India Minimum Surface air Temperature Anomaly | 1. Deesa 2.Rajko 3. Guna 4. Bikaner 5. Akola 6. Barmer | 16th April to 15th May | -0.63 |
| 3 | Zonal Wind Anomaly at 1000hpa over Equatorial South Indian Ocean | 1-15 may | 10S-0, 80E-100E | 0.52 |
| 4 | OLR Anomaly Over Indo-China | 1-15 may | 17.5N-27.5N, 95E-105E | 0.43 |
| 5 | OLR Anomaly Over Southwest Pacific | 1-15 may | 30S,20S, 145E-160E | -0.54 |
| 6 | Pre-Monsoon Rainfall Peak Date | Pre-monsoon | South Peninsula (8N-13N, 74E-78E) | 0.65 |
The PC analysis was applied over the predictor set containing all the 6 predictors for the 26 years (1975-2000) and first 3 principle components(PC1, PC2 and PC3) explaining about 79% of the total variability of the predictor set were retained for further analysis. A multiple linear regression model was then developed using the retained 3 PCs as the input variables and MOK as the predictand. Model was developed using the same 26 years (1975-2000). This model was then used for predicting the MOK.